NonStop S-Series Server Description Manual (G06.24+)
Memory Addressing and Access
HP NonStop S-Series Server Description Manual—520331-003
4-8
Address Formats
Address Formats
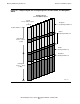
The 32-bit address used for each of the four addressing spaces is identified by the bit
pattern of the first one, two, or three bits. See Figure 4-4. The one-bit pattern of “0”
specifies a nonprivileged space address (relative). The three-bit pattern of “100” or
“101” specifies a Kseg0 or Kseg1 address, respectively (physical). The two-bit pattern
of “11” specifies a Kseg2 address.
Any address with a 0 in the most significant bit position is a nonprivileged space
address. All the remaining bits are then available to specify a particular byte within that
space. Bits 1 through 6 specify a region, 7 through 14 specify a unitary segment, 15
through 17 a page, and 18 through 31 a byte. Any address with a 1 in the most
significant bit position is in the higher-address half of the process address space and
therefore in the privileged space.
In nonprivileged space, it is sometimes convenient to ignore the region boundaries and
treat bits 1 through 14 of the relative address as a relative segment number.
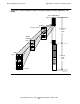
All addresses in the privileged space begin with a 1 in the most significant bit position.
If the next-most significant bit is a 0, the address is a physical address, either within the
Kseg0 space or within the Kseg1 space. If the third-most significant bit is a 0, the
address is within Kseg0; if that bit is a 1, the address is within Kseg1. In either case,
the field consisting of bits 3 through 17 specifies a frame in physical memory, and the
field consisting of bits 18 through 31 specifies the byte within that frame. (Physical
memory does not use the concept of segments, as virtual memory does.)
If the two most significant bits are both 1, the address is within the Kseg2 space. Like
the nonprivileged space, Kseg2 addresses are organized into regions, unitary
segments, and pages. Bits 2 through 6 specify a region, 7 through 14 specify a unitary
segment, 15 through 17 a page, and 18 through 31 a byte. (Unlike the nonprivileged
space, only five bits are available to specify a region, because bit 1 is used to
distinguish the Kseg2 address from Kseg0 and Kseg1 addresses; thus 32 regions are
available instead of 64.)