NonStop S-Series Server Description Manual (G06.24+)
Memory Addressing and Access
HP NonStop S-Series Server Description Manual—520331-003
4-12
First Four Relative Segments
First Four Relative Segments
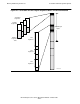
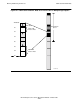
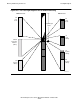
Figure 4-6 shows addressing details for the first four regions, particularly the first
region. Hexadecimal starting addresses are indicated for the regions and the first five
relative segments, 0 through 4.
Relative segment 0 is the TNS user data segment, which, for TNS processes, provides
relative addressing for process global variables and the TNS data stack. Relative
segments 1, 2, and 3 are skipped. Then, the current selectable segment begins at
relative segment 4 (hexadecimal address 00080000).
The reason for skipping relative segments 1, 2, and 3 is that these segment numbers
are reserved for backward compatibility. In the TNS architecture, these are assigned
to system data segment, current code segment, and latest user code segment,
respectively. In the NonStop S-series processors, most references to system data are
through Kseg0 addresses, and thus references to relative segment 1 are not usually
needed. Similarly, current code and user code (that is, the last-used user code
segment) also are not usually needed, because all code segments are simultaneously
available in the NonStop S-series processors. Thus these three relative segment
numbers are not normally used, but they do work—for those TNS applications that
have not been converted to remove hard-coded references.
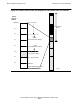
Because there are 256 unitary segments in a region, a selectable segment that
consists of more than 252 unitary segments crosses at least one region boundary.