NonStop S-Series Server Description Manual (G06.24+)
TNS Execution Modes
HP NonStop S-Series Server Description Manual—520331-003
6-22
Byte Addressing in the Data Segment
Byte Addressing in the Data Segment
Two bytes can be stored in a 16-bit word. The most significant byte in a word occupies
the left half (bits 0 through 7), and the least significant byte occupies the right half
(bits 8 through 15).
Memory reference instructions always specify a TNS-word displacement for direct
addressing, including those used for byte addressing (LDB, STB, LBP). For direct
addressing, the left byte of the word at the displacement location is the addressed
byte.
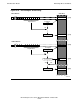
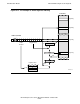
When indirect addressing is used, the word at the displacement location holds a byte
address. The processor converts this byte address to a word address and bit field in
that word, as shown in Figure 6-13. In other words, bit 15 of the byte address is
extracted and used to specify left byte (0) or right byte (1); the remaining 15 bits are
logically shifted right by one bit to form the word address. In this case, byte-
addressable locations in the data segment start at BYTE[0] and extend through
BYTE[65535], ending at word location 32767.
Because one bit of a 16-bit byte address must be used to specify left or right byte,
15 bits are left to specify a word. That limits the byte addressing range of a 16-bit byte
address to the first half of the data segment.
Figure 6-13. Byte Addressing in the Data Segment Is Restricted to Half Segment
150
Byte Address to Word Address Conversion
Byte Address [0:65535]
If 0: Word.<0:7>
If 1: Word.<8:15>
Word Address [0:32767]
0
015
Byte Address
Upper Limit of
Byte Addressing
Word [0]
Word [1]
Word [2]
Word [32766]
Word [32767]
7 8
[0]
[2]
[4]
[65,532]
[65,534]
[1]
[3]
[5]
[65,533]
[65,535]
VST278.vsd