NonStop S-Series Server Description Manual (G06.24+)
TNS Execution Modes
HP NonStop S-Series Server Description Manual—520331-003
6-23
Byte Addressing in the Data Segment
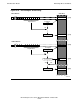
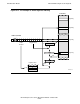
In the example shown in Figure 6-14, indirect addressing is used to get a byte address.
The (word) displacement value is 2, which means that the address is in G[2]. In this
case, G[2] contains the value 12345, which is a byte address. To convert that to a
word address and byte specifier, the value is divided by 2, giving a word address of
6172 with a remainder of 1. The remainder of 1 specifies the right-hand byte, as
indicated in the figure.
For byte addressing in the data segment, the displacement field specifies a word
displacement from G[0] to a location in the global area. In the case of direct
addressing, the left byte of that location contains the addressed byte. In the case of
indirect addressing, the content of the word at the specified displacement location
contains a byte address that specifies a particular byte (either left or right) in the first
half of the data segment.
Figure 6-14. Indirect Byte Addressing in the Data Segment Can Specify Odd
Bytes
G [0]
00000010
Indirect, No Index
Displacement
0
G-Relative
Addressing
Mode
1
Index
Reg.
(none)
G [2]
G [6172]
12345 / 2 = 6172, r = 1
1 = Right Half
00
12345
VST279.vsd