NonStop S-Series Server Description Manual (G06.24+)
TNS Execution Modes
HP NonStop S-Series Server Description Manual—520331-003
6-36
Data Segment Addressing Modes
Data Segment Addressing Modes
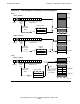
All direct addressing in the data segment is relative to one of the three addressing
bases: G, L, or S. Memory reference instructions for data contain a 9-bit address field
for specifying one of the three addressing bases and a relative displacement from that
base. Four addressing modes are provided for addressing relative to these bases. (A
fifth mode, SG-relative addressing, exists for addressing relative to a base in the
system data segment; that mode is described earlier in this section.)
For addressing in the user data segment, the addressing modes are G-relative,
L-plus-relative, L-minus-relative, and S-minus-relative. The following paragraphs
describe these four addressing modes. Each is illustrated in Figure 6-21. The
illustration also defines the bit patterns used in instructions that use these modes.
G-Relative Mode This mode addresses the first 256 locations in the global
area, G[0:255]. The G-relative mode is indicated when bit
7 of a memory reference instruction is equal to 0; bits 8:15
specify a positive word displacement from G[0].
L-Plus-Relative Mode This mode addresses the first 128 words of a procedure’s
local data area, L[0:127]. The L-plus-relative mode is
indicated when bits 7:8 of a memory reference instruction
are equal to 10 (binary); bits 9:15 specify a positive word
displacement from the current L[0]. The processor
calculates a G-relative address by adding bits 9:15 to the
contents of the L register.
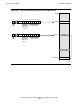
L-Minus-Relative Mode This mode addresses the 32 words just below and
including the word pointed to by the current L register
setting,
L[–31:0]. (This area is used for accessing procedure
parameters.) The L-minus-relative addressing mode is
indicated when bits 7:10 of a memory reference instruction
are equal to 1110 (binary); bits 11:15 are a negative word
displacement from the current L[0]. The processor
calculates a G-relative address by subtracting bits 11:15
from the contents of the L register.
S-Minus-Relative Mode This mode addresses the 32 words just below and
including the current top-of-stack word, S[–31:0]. (This
area is used for a subprocedure’s sublocal data and for
temporary storage of the register stack contents by the
PUSH and POP instructions.) The S-minus-relative mode
is indicated when bits 7:10 of a memory reference
instruction are equal to 1111 (binary); bits 11:15 are a
negative word displacement from the current S[0]. The
processor calculates a
G-relative address by subtracting bits 11:15 from the
contents of the S register.