NonStop S-Series Server Description Manual (G06.24+)
Introduction
HP NonStop S-Series Server Description Manual—520331-003
1-6
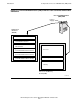
Internal Arrangement of System Enclosures
Internal Arrangement of System Enclosures
Processor enclosures and I/O enclosures are very similar in their internal arrangement,
and the generic term that describes both is system enclosure. The primary difference
is that, for I/O enclosures, processors do not exist on the CRUs installed in locations
50 and 55. IOMF CRUs are installed in slots 50 and 55 instead. Another difference is
that ServerNet expansion boards (SEBs) or modular ServerNet expansion boards
(MSEBs) cannot be installed in I/O enclosures.
Figure 1-3 illustrates a typical internal arrangement for the system enclosures from
both the appearance side and the service side. (The illustration shows a NonStop
S7000 processor enclosure.)
Slots 51 through 54 can contain four ServerNet adapters. In the case of a processor
enclosure, these slots could instead contain four ServerNet expansion boards, or two
of each. (The functions of ServerNet expansion boards are discussed under Expansion
to Second Processor Enclosure on page 1-16.)
Sixteen 3.5-inch disk drives can be accommodated in slots 01 through 08 and 11
through 18, using two internal SCSI buses.
Whether slots 50 and 55 contain processor multifunction (PMF) CRUs (see page 1-8)
or I/O multifunction (IOMF) CRUs (see page 1-20), these slots each provide one
differential SCSI port for connection to external SCSI devices and one Ethernet port.
Note. SEBs provide connections that link one system enclosure to another. A modular
ServerNet expansion board (MSEB) is a SEB that uses plug-in cards (PICs) to provide a
choice of cable media (ECL, fiber-optic, or serial copper) for routing ServerNet packets. In
addition, only MSEBs can be used for clustering interconnections. In cases where only
MSEBs are permissible, this manual specifically uses the MSEB acronym; otherwise, the SEB
acronym is used as a generic term for both kinds of boards.