NonStop S-Series Server Description Manual (G06.24+)
TNS Instruction Set
HP NonStop S-Series Server Description Manual—520331-003
11-37
Definitions of TNS Instructions
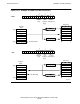
QSUB (000241). Quadruple Subtract. The quadrupleword integer contained in DCBA
is subtracted in quadrupleword integer form from the quadrupleword integer in HGFE.
Both operands are deleted, and the quadrupleword result is pushed onto the stack.
Overflow is set if the result is greater than 2
63
–1 or less than –2
63
. Carry is set if no
borrow-out occurs. Condition Code is set on the result.
QUP (00025-). Quadruple Scale Up. The operand value in DCBA is multiplied by a
specified power of ten (1, 2, 3, or 4), and the new value replaces the former contents of
DCBA. Overflow is set if the result is greater than 2
63
–1 or less than –2
63
. Condition
Code is set on the result. For binary coding details, see Table B-6 on page B-7.
RCLK (000050). Read Clock. This instruction reads the quadrupleword microsecond
counter (located in the system data segment), adds the instantaneous value of the
14-bit hardware microsecond counter to it, and pushes the result onto the register
stack. Note that because the software counter is updated only every 10 milliseconds
(each time the hardware counter rolls over), adding the hardware count to it provides
an accurate clock indication at the instant that RCLK is executed. This instruction is
nonprivileged.
RCPU (000051). Read CPU Number. This instruction reads this processor’s
processor number from bits 0:7 of INTB and pushes this value onto the register stack.
This is a privileged instruction.
RDE (000024). Read ENV Into A. The contents of the Environment (ENV) register are
pushed onto the register stack.
RDP (000025). Read P Into A. The contents of the Program Counter (P) are pushed
onto the register stack.
RSUB (025---). Return From Subprocedure. This instruction is used to return from a
subprocedure called by a BSUB instruction. The instruction assumes that the return
address is on the top of the memory stack (indicated by S) and returns control to that
address. S is set to S – S^decrement. “S^decrement” can be any number from 0 to
255. However, to delete the return address from the stack, it must be at least 1. For
binary coding details, see Table B-3
on page B-3.
RSW (000026). Read the Switch Register Into A. The contents of the processor’s
Switch register (always zero on TNS/R processors) are pushed onto the register stack.
Condition Code is set. This instruction is nonprivileged.
SBA (000365). Store Byte via A. The byte in B is stored into the effective memory
location pointed to by the byte address in A. Both B and A are then deleted. SBA
accesses the current data segment only.
SBAR (00017-). Subtract A From a Register. A is subtracted in signed integer form
from the register pointed to by the Register field of the instruction. A is deleted from
the stack. Overflow is set if the result is greater than 32767 or less than –32768.
Carry can be set, meaning no borrow. Condition Code is set on the result. For binary
coding details, see Table B-5
on page B-5.