NonStop S-Series Server Description Manual (G06.24+)
TNS Instruction Set
HP NonStop S-Series Server Description Manual—520331-003
11-38
Definitions of TNS Instructions
SBAS (000355). Store Byte via A Into System. The byte in B is stored into the
effective memory location pointed to by the byte address in A. Both B and A are then
deleted. A refers to an address in the system data segment.
SBRA (00015-). Subtract Register From A. The contents of the register pointed to by
the Register field of the instruction are subtracted in integer form from register A.
Overflow is set if the result is greater than 32767 or less than –32768. Carry can be
set, meaning no borrow. Condition Code is set on the result. For binary coding details,
refer to Table B-5 on page B-5.
SBU (1266--). Scan Bytes Until. The SBU instruction expects A.<8:15> to contain a
test byte and B to contain the byte address of the string to be scanned. The segment
to be used is determined by the “S” field of the instruction and by the DS, CS, and LS
bits of the ENV register. If the source address is specified as current code segment,
the byte address is taken to be in the same 64K-byte half of the code space as the
current P register value. If the source address is specified as latest user code
segment, the byte address is taken to be in the lower 64K-byte half of that segment.
The “RL” field of the instruction determines whether the scan address will be
incremented (“RL” = 0) or decremented (“RL” = 1) after each comparison. The scan is
terminated when either a null byte is found in the string or the test byte matches a byte
in the string. The Carry (K) bit is set in the ENV register when null byte termination
occurs. In either case, B points to the byte address that caused the scan to cease. RP
is set to the “RP” field of the instruction at termination. For binary coding details, refer
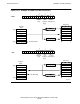
to Table B-3 on page B-3. Figure 11-7 on page 11-9 provides a comparison of
ascending and descending directions.
SBW (1264--). Scan Bytes While. The SBW instruction expects A to contain a
comparison byte in bits 8:15 and B to contain the byte address of the string to be
scanned. The segment to be used is determined by the “S” field of the instruction and
by the DS, CS, and LS bits of the ENV register. If the source address is specified as
latest user code segment, the byte address is taken to be in the lower 64K-byte half of
that segment. The “RL” field of the instruction determines whether the source address
will be incremented (“RL” = 0) or decremented (“RL” = 1) after each comparison. The
scan is terminated when either a null byte is found in the string or a byte in the string
does not match the test byte in A. When null byte termination occurs, the Carry (K) bit
in the ENV register is set. In either termination case, B points to the byte address that
caused termination. RP is set to the “RP” field of the instruction at instruction
termination. For binary coding details, refer to Table B-3 on page B-3 . Figure 11-7 on
page 11-9 provides a comparison of ascending and descending directions.
SBX (000407). Store Byte Extended. The byte in bits 8 through 15 of C is stored into
the memory location specified by the 32-bit byte address in registers B and A. C, B,
and A are then deleted.
SBXX (0257--, 0267--). Store Byte Extended, Indexed. The byte contained in
B.<8:15> is stored into a computed memory location. The memory address is obtained
as follows. The displacement value (0 through 63) in bits 10 through 15 of the
instruction word is added to a base value, which is either G[0] (coded 0257--) or the
current L register value (coded 0267--); the data word so indicated is assumed to be