NonStop S-Series Server Description Manual (G06.27+)
TNS Data Formats and Number Representations
HP NonStop S-Series Server Description Manual—520331-004
3-11
Instructions for Decimal and Floating-Point
Arithmetic
The bit-level representations of TNS and IEEE floating-point values are incompatible.
The two formats have different precisions and exponent ranges in their 32-bit sizes,
and different precisions and exponent ranges in their 64-bit sizes.
For a description of the IEEE representations as used on NonStop S-series servers,
see Chapter 7, “FPU Overview,” in MIPS RISC Architecture by Gerry Kane and Joe
Heinrich.
The fraction of a TNS-format floating-point number is always normalized, to be greater
than or equal to 1 and less than 2. The high-order integer bit is therefore dropped and
assumed to have the value of 1. During all calculations, the sign is temporarily
removed and the assumed integer bit reinserted. The integer plus the 22 fraction bits of
a floating-point number are equivalent to 6.9 decimal digits; the 55 bits of an extended
floating-point number are equivalent to 16.5 decimal digits. (Both formats are shown in
Figure 3-4.) If the value of the number to be represented is zero, the sign is 0, the
fraction is 0, and the exponent is 0.
The fraction of a floating-point number is a binary number with the binary point always
between the assumed integer bit and the high-order fraction bit. The exponent part of
the number, bits 7 through 15 of the low-order word, indicates the power of 2 multiplied
by 1 plus the fraction. This field can contain values from 0 through 511. To express
numbers of both large and small absolute magnitude, the exponent is expressed as an
excess –256 value; that is, 256 is added to the actual exponent of the number before it
is stored. The exponent range is therefore actually –256 through +255.
The sign of a floating-point number is explicitly given in the high-order bit; a 0 is
positive, and a 1 is negative. Unlike integers, which use two’s complement, negating a
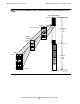
Figure 3-4. Formats for TNS Floating-Point and Extended Floating-Point Data
TNS-format floating-point doubleword:
TNS-format extended floating-point quadrupleword:
01516 31
Sign
22 23
Fraction (22 Bits)
Exponent (9 bits)
01516 31
Word 0
Word 1
Word 2
Word 3
22 23
Exponent (9 bits)
Fraction (54 Bits)
Sign
Fraction (54 Bits)
VST230.vsd