NonStop S-Series Server Description Manual (G06.27+)
Memory Addressing and Access
HP NonStop S-Series Server Description Manual—520331-004
4-10
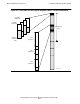
Selectable and Flat Logical Segments
Selectable and Flat Logical Segments
Data address space for a process is allocated in virtual memory by one or more
SEGMENT_ALLOCATE_ procedure calls. Each call allocates a logical segment that
is of a specifiable size.
A logical segment can be either one of two kinds: a selectable segment or a flat
segment. These are compared in Figure 4-5, and the choice is made by a parameter
supplied to the SEGMENT_ALLOCATE_ call. (A selectable segment previously was
sometimes called an extended data segment or extended segment.)
Any number of selectable segments can be allocated; however, they all share the
same address space, hexadecimal addresses 00080000 through 07FFFFFF. Thus,
only one selectable segment can be in use at any given time. The selection is made
with a SEGMENT_USE_ procedure call.
The maximum size of a selectable segment is 127.5 megabytes, the first half
megabyte being reserved for compatibility with earlier TNS systems (see next topic).
All selectable segments begin at the start of relative unitary segment 4 and can
include, as a maximum, relative unitary segment 1023, as shown in the figure.
Flat segments, on the other hand, have distinct addresses. The operating system
allocates distinct addresses within the nonprivileged area starting at a fixed upper
boundary of 4E000000 and proceeding downward to a variable lower boundary. Flat
segments can theoretically be up to 1120 megabytes in size and need not begin on a
region boundary.
Because flat segments have distinct addresses, they do not need to be made current
with a SEGMENT_USE_ procedure call. They are continuously available to the
process.