NonStop S-Series Server Description Manual (G06.27+)
Memory Addressing and Access
HP NonStop S-Series Server Description Manual—520331-004
4-16
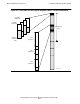
Last Eight Regions
Last Eight Regions
All of the user code, and user library, and shared run-time library (SRL) allocations
are accessed within the code regions, as illustrated in Figure 4-8. These are the last
eight regions (256 megabytes) in the nonprivileged space. In addition, the system
library is also included in the code regions of each process.
With few exceptions (Debug, for example), writing is not permitted into any of the code
regions. This restriction is under hardware control, cooperatively with system software.
(However, privileged software can write anywhere that is physically addressable—
through Kseg0 or Kseg1.)
The number of regions allocated to the various kinds of code depends on the kind of
process that was created: either native or TNS.
For a native process, two full regions (32 megabytes each) are available for user code
allocation. User code allocation for a native process is designated as UCr, signifying
“user code RISC.”
For a TNS process, one full region is dedicated to each kind of code area. That is, one
region is for user code (UC), one for user library (UL). Although all regions have 256
segments, TNS architecture limitations restrict the maximum number of unitary code
segments that can exist in each TNS code area. (Note lighter-shaded areas in the UC,
UL, and SL areas.) The user code region can contain up to 32 unitary segments, and
the user library can contain up to 32 unitary segments. The remainder of each of these
regions (shaded darker in the figure) is available for accelerated code, if present.
The system library has one region available for native code, designated SLr, and one
for TNS code, designated SL. Unlike system code, the system library (SLr and SL)
contains some nonprivileged code and therefore must be included in the nonprivileged
space. Much of the system library is actually coded as native procedures in the SLr
region; calls to callable procedures from TNS or accelerated mode are routed through
SL to SLr by to-RISC shells (discussed later).
System code (SC and SCr) is located in physical memory—specifically, in Kseg0 of the
privileged space. The use of Kseg0 is described later, and so system code does not
appear in this figure.