NonStop S-Series Server Description Manual (G06.27+)
Memory Addressing and Access
HP NonStop S-Series Server Description Manual—520331-004
4-26
Physical Memory Addressing
Physical Memory Addressing
The preceding topics describe the nonprivileged space. This and the next two topics
describe the privileged space.
As indicated earlier, privileged space addresses are signified by a 1 in the most
significant bit position of the 32-bit address word.
For segment-numbering purposes, physical addresses can be considered to be a
special form of absolute address. Thus the entire privileged space has a range of
16,384 absolute segments, numbered from 0 through 16,383.
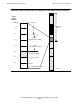
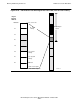
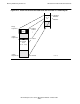
Absolute segments 0 through 4095 provide a range of physical addresses to address
physical memory through Kseg0. This correspondence is illustrated in Figure 4-12.
Similarly, absolute segments 4096 through 8191 provide a range of addresses to
address physical memory through Kseg1. In each case, the addressing range is 512
megabytes.
Kseg0 and Kseg1 addresses correspond directly to the physical memory designated
by the low-order 29 bits of the address. That is, byte 0 of absolute segment 0 (in
Kseg0) and byte 0 of absolute segment 4096 (in Kseg1) both designate byte 0 of
physical memory.
The difference between Kseg0 addressing and Kseg1 addressing is that Kseg0 uses
the data and instruction caches (the more normal case), whereas Kseg1 does not (and
is the more exceptional case). The use of caches is described later, when access
techniques are described.
Because installed hardware memory can exceed 512 megabytes, Kseg0 and Kseg1
can have their correspondence with only the first 512 megabytes of installed memory.
Access to memory in excess of 512 megabytes can be achieved only by mapping
through page tables—that is, through nonprivileged space or Kseg2.
Within the entire 4-gigabyte range of the process address space, the Kseg0
hexadecimal addresses are 80000000 through 9FFFFFFF. For Kseg1, the range is
A0000000 through BFFFFFFF.
Actual use of Kseg0 space is described in the next topic.