NonStop S-Series Server Description Manual (G06.27+)
Instruction Processing Environments
HP NonStop S-Series Server Description Manual—520331-004
5-4
Stacks for Native and TNS Processes
Stacks for Native and TNS Processes
Data stacks are a principal resource of each process. They provide a historical record
of procedure calls, as well as the local addressing environment of procedures,
including some of the parameters passed between procedures.
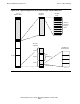
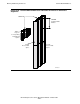
In the execution of a native process, two different stacks are used, depending on
whether or not privileged mode is in effect. The illustration in Figure 5-2 shows the
locations of the two stacks.
The main stack is the normal stack area of a nonprivileged native process. This stack
area begins at the end of the 4E region, just below virtual address 50000000
(hexadecimal). This address is defined by the operating system. The stack grows
from higher addresses to lower addresses. The default maximum size of the main
stack varies with the kind of process. The largest main stack currently defined is one
full unitary segment (128K bytes).
The privileged stack is used for native mode procedures running privileged. It is the
normal stack area for privileged native processes. Native procedures that are not
callable execute on the same stack as their caller. For nonprivileged processes,
execution switches to the privileged stack when a native callable procedure is entered.
Such a switch requires that the procedure’s arguments be moved to the privileged
stack from the main stack.
The privileged stack begins at the end of the 5E region, just below virtual address
60000000 (hexadecimal). This address is defined by the operating system. Like the
main stack, the privileged stack grows from higher addresses to lower addresses.
When a process is not privileged, the privileged stack is always considered to be
empty; any contents will be overwritten. The only exit from the privileged stack to the
main stack is through a return from a callable procedure that was called from a
nonprivileged procedure. The switch back to the main stack is done as part of the
privilege transition return.
For TNS processes, there is an additional stack, termed the TNS user data stack. It
contains data used by TNS procedures and is located in the first half of the first unitary
segment of the first region. This stack is in addition to those described above, because
the TNS process switches to native mode, using the main or privileged stack, when
calling RISC procedures in the system library.
For native processes, global data is allocated at the beginning of the 08 region. For
TNS processes, global data is allocated immediately preceding the TNS user data
stack.