NonStop S-Series Server Description Manual (G06.27+)
TNS Execution Modes
HP NonStop S-Series Server Description Manual—520331-004
6-60
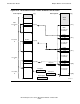
Retrieving a Returned Value
Retrieving a Returned Value
The preceding topic described a function procedure that is capable of returning a value
to a caller. This topic describes the overall sequence of using that procedure in the
context of a call and return. Refer to Figure 6-33.
Suppose a call is made to the procedure “f”, as follows:
z := i + j - f(5);
That is, subtract the square of 5 from the sum of the contents of the variables “i” and
“j”, then store the result in the variable “z”. The name “f” here means that the
procedure “f” should be called, and “5” is the parameter passed to that procedure.
Variables “i”, “j”, and “z” are local variables at L[1], L[2], and L[3], respectively. The
instructions to perform this operation are:
LOAD L +001 ! load i
LOAD L +002 ! load j
IADD ! i + j
LDI +005 ! load parameter to f
PUSH 711 ! push sum and parameter onto memory stack
PCAL f ! procedure call to f
STAR 1 ! move returned value from R[0] to R[1]
POP 100 ! bring saved sum back to R[0]
ISUB ! subtract returned value from i+j sum
STOR L +003 ! store result into z
The first three instructions calculate the sum “i” + “j” and leave the result in R[0]. The
LDI +005 instruction loads the parameter to “f” to the top of the register stack at R[1].
The PUSH instruction pushes R[0:1] onto the memory stack. Following the PUSH, the
two top-of-memory-stack locations contain:
S[-1] = sum of i + j
S[0] = 5, the parameter to f
This clears the register stack for use by the procedure, which now is invoked by the
PCAL instruction. (The PCAL instruction specifies the PEP number of the “f”
procedure.) On the return from “f”, R[0] of the register stack contains the square of 5.
The STAR instruction moves the return value in the R[0] register stack location to R[1]
in preparation for the subtraction from the sum of “i” + “j”.
The POP 100 instruction brings the sum of “i” + “j” (calculated previously) into R[0] and
sets RP to 1 (to point to the returned value).
The ISUB instruction subtracts the return value of “f” from the sum of “i” + “j”. The
STOR instruction stores the result in the variable “z”, which is the location L[3], and RP
becomes 7 (empty).