NonStop S-Series Server Description Manual (G06.27+)
Introduction
HP NonStop S-Series Server Description Manual—520331-004
1-16
Expansion to Second Processor Enclosure
Expansion to Second Processor Enclosure
Most NonStop systems require that several processor enclosures be connected
together. Such interconnections are provided through specialized, plug-in boards in
processor enclosures that expand the ServerNet fabric from one enclosure to another.
These boards, if present, are installed in pairs in slots 51 through 54 of a processor
enclosures. See Figure 1-3 on page 1-7.
There are two kinds of such boards. The original and simpler version is called a
ServerNet expansion board (SEB), which uses six-port routers. The later version is
called a modular ServerNet expansion board (MSEB). The MSEB uses 12-port routers
(though only seven ports are currently assigned) and is called modular because it
accepts a variety of plug-in cards (PICs), or modules, that permit easy adaptability to
different interconnection protocols. As mentioned previously, in this manual and in
other ServerNet documentation, SEB is often used as a generic term to denote the
basic function.
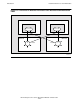
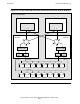
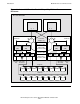
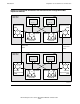
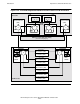
Figure 1-9 shows how a pair of SEBs can be used to connect one processor enclosure
to another.
The main logic component of a SEB is a router that is additional to the one already
present on the MFIOB. SEBs are always added in pairs because one is needed for the
X fabric and one is needed for the Y fabric.
In each case, the router connection from the MFIOB that connects to an SEB is the
router port that was shown unused in Figure 1-7 and Figure 1-8. The four downward-
pointing arrows from the MFIOB routers connect to the SCSI bus and I/O slots like the
example shown in Figure 1-8 on page 1-15.
The required cables for interconnecting the two processor enclosures are shown with
bold lines in the example in Figure 1-9
. One cable interconnects the X routers on one
SEB in each of the processor enclosures, and the other cable interconnects the Y
routers.
Note that four unused router ports are available on each of the SEBs. These ports can
be used for expanding either, or both, the number of processor enclosures and the
number of I/O enclosures. Expansions of both kinds are the subject of the remaining
topics in this section.
Note. For clarity, the I/O details are omitted in Figure 1-9. As explained in the preceding topic
(Maximum Processor Enclosure I/O), I/O configuration details vary. For example, MFIOB
boards use six-port routers and therefore have three, rather than four, router ports for internal
I/O logic.