NonStop S-Series Server Description Manual (G06.27+)
TNS Instruction Set
HP NonStop S-Series Server Description Manual—520331-004
11-29
Definitions of TNS Instructions
LDI (100---). Load Immediate Operand Into A. The immediate operand is pushed onto
the stack, with the sign bit propagating into the high-order bits. Condition Code is set.
(For binary coding details, refer to Table B-2 on page B-2.)
LDIV (000203). Logical Divide CB by A, leaving the remainder in B. The 32-bit
positive (unsigned) integer in C and B is divided by the 16-bit positive integer in A. The
divisor and dividend are deleted from the stack, the remainder is pushed onto the stack
(B), and the quotient is pushed onto the stack (A). Overflow is set if the original C is
greater than or equal to the original A. Condition Code is set, based on the quotient in
A.
LDLI (005---). Load Left Immediate Operand Into Bits 0:7 of A. The immediate
operand, shifted left eight places, is loaded into A, with the sign bits propagating into
the low-order bits of A. Condition Code is set. (For binary coding details, refer to
Table B-2 on page B-2.)
LDRA (00013-). Load A From a Register. The contents of the register pointed to by
the Register field of the instruction are pushed onto the stack. Condition Code is set.
(For binary coding details, refer to Table B-5 on page B-5.)
LDX (-3x---). Load Index Register From Data Space. The index register specified by
the “x” field of the instruction is loaded with the contents of the effective memory
address. Condition Code is set. Figure 11-1 on page 11-2 shows the instruction word
format for memory data reference instructions, such as LDX. For binary coding details,
refer to Table B-1 on page B-1.
LDXI (10----). Load Index Register With Immediate Operand. The index register
specified by the “x” field of the instruction is loaded with the immediate operand, and
the sign bit propagates into the high-order bits. Condition Code is set. (For binary
coding details, refer to Table B-2 on page B-2.)
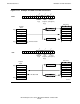
LLS (0300--). Logical Left Shift. If the shift count field is zero, the (unsigned) word
contained in B is shifted left by the dynamic count contained in A. A is then deleted
from the stack. However, if the shift count field is not zero, A is shifted left by that
number. Condition Code is set. Refer to Figure 11-4
on page 11-5 for a comparison of
logical (unsigned) shifts and arithmetic (signed) shifts.
LMPY (000202). Logical Multiply A Times B. A and B are multiplied as 16-bit positive
(unsigned) integers. A and B are then replaced by the doubleword result, with the
least significant half in A. Overflow is implicitly cleared. Condition Code is set.
LNEG (000204). Logical Negate A. The unsigned value in A is converted to its two’s
complement. Carry is set if the original value of A is zero. Condition Code is set.
LOAD (-40---). Load A From Data Space. The contents of the effective address
memory location are pushed onto the stack. Condition Code is set. For binary coding
details, refer to Table B-1
on page B-1.
LOR (000011). Logical OR A With B. A and B are merged by a logical inclusive OR.
A and B are deleted and the result pushed onto the stack. Condition Code is set. (For
an example, see Figure 11-5 on page 11-6.)