NonStop S-Series Server Description Manual (G06.27+)
TNS Instruction Set
HP NonStop S-Series Server Description Manual—520331-004
11-32
Definitions of TNS Instructions
count, B to contain the source byte address, and C to contain the destination byte
address. The source and destination segments to be used are specified by the “S” and
“D” fields of the instruction and by the DS, CS, and LS bits of the ENV register. The
“RL” field of the instruction determines whether the source and destination addresses
will be incremented (“RL” = 0) or decremented (“RL” = 1) after each move. The “RP”
field of the instruction is the value to which RP is set upon instruction end. The move
is made one byte at a time from the source to the destination. After each byte transfer,
the addresses are decremented or incremented and A is decremented. If A is equal to
zero, the instruction ends; otherwise the next byte is moved. If the source is specified
as the current code segment and the P register currently indicates an address in the
upper half of the code segment (bit 0 of P = 1), %100000 is added to the computed
address, so that the source address is always relative to whichever half of the segment
P currently indicates. If the source is specified as the latest user code segment, the
16-bit source address indexes the lower 64K bytes of that segment. For binary coding
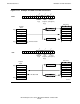
details, refer to Table B-3 on page B-3. Figure 11-7 on page 11-9 provides a
comparison of ascending and descending directions.
MOVW (026---). Move Words. This instruction transfers a specified number of words
from one area of memory to another. The instruction expects A to contain a word
count, B to contain the source word address, and C to contain the destination word
address. The source and destination segments to be used are specified by the “S” and
“D” fields of the instruction and by the DS, CS, and LS bits of the ENV register. The
“RL” field of the instruction determines whether the source and destination addresses
will be incremented (“RL” = 0) or decremented (“RL” = 1) after each move. The “RP”
field of the instruction is the value to which RP is set upon instruction end. The move
is made one word at a time from the source to the destination. After each word
transfer, the addresses are decremented or incremented and A is decremented. If A is
equal to zero, the instruction ends; otherwise the next word is moved. For binary
coding details, refer to Table B-3 on page B-3. Figure 11-7 on page 11-9 provides a
comparison of ascending and descending directions.
MVBX (000417). Move Bytes Extended. This instruction transfers a specified number
of bytes from one area of extended memory to another. The instruction expects A to
contain a byte count, CB to contain a 32-bit source byte address, and ED to contain a
32-bit destination byte address. The move is made one byte at a time from the source
to the destination. After each byte transfer, the addresses are incremented and A is
decremented. If A is equal to zero, the instruction ends; otherwise the next byte is
moved. All five words are deleted from the stack when the instruction ends.
NOP (000000). No Operation.
NOT (000013). One’s Complement A. The word contained in register A of the stack is
converted to its one’s complement. Condition Code is set. (For an example, see
Figure 11-5
on page 11-6.)
NSAR (00012-). Nondestructive Store A Into a Register. The A register is stored in
the register pointed to by the Register field of the instruction. (For binary coding
details, refer to Table B-5
on page B-5.)