NonStop Systems Introduction
The Relational Database Management System
NonStop Systems Introduction—527825-001
4-12
Portability of SQL/MX Applications
Portability of SQL/MX Applications
SQL/MX applications are applications that contain embedded SQL statements within
host language code. SQL/MX applications are easy to port to the systems of other
vendors because they are written in languages that conform to industry standards:
•
Embedded SQL is based on ANSI-standard and ISO-standard SQL.
•
HP COBOL, C, and C++ are based on the ANSI standards for those languages.
Another advantage of using industry-standard languages for NonStop database
applications is that programmers who have come to the NonStop application
environment from other environments are already trained to use SQL and the other
languages.
Integration With the Operating System
SQL/MX is fully integrated with the operating system for efficient operations. You use
standard system naming conventions for SQL catalogs, tables, views, collations, and
programs. In addition, a number of system utilities and special SQL/MX utilities
provide efficient system management and control for SQL/MX applications.
This system-level integration also contributes to performance. By adding processors to
your NonStop server, you can dramatically increase performance.
Data Distribution
SQL/MX databases are well suited for distributed applications because SQL/MX tables
can be partitioned across multiple disk volumes in a system or across multiple systems
in a network. Logically, the table is a single entity, but physically it is split up over many
locations. With such a partitioning scheme, data pertinent to a locality can be near its
users, but authorized users at other locations can access the data when they need to.
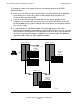
Figure 4-7 on page 4-13 shows an SQL/MX table whose primary key is a customer
number. This table is partitioned across an HP network with three nodes, with each
node using a NonStop server.
In Figure 4-7, the data is distributed as follows:
•
The system A node contains two partitions of this table, each on a separate disk
drive. The first partition contains the rows for customers 1-2500, and the second
partition contains the rows for customers 2501-5000.
•
The node that uses system B has one table partition containing rows for customers
5001-7500.
•
The node using system C has a single partition containing customer numbers
7501-10000.