OSF DCE Application Development Guide--Core Components
OSF DCE Application Development Guide—Core Components
11.1.5 Overview of DCE RPC Development Tasks
The tasks involved in developing an RPC application resemble those involved in
developing a local application. As an RPC developer, you perform the following basic
tasks:
1. Design your application, deciding what procedures you need, which will be remote
procedures, and how the remote procedures will be grouped into RPC interfaces.
2. Use the Universal Unique Identifier (UUID) generator to generate a UUID for each
new interface.
3. Use the IDL to describe the RPC interfaces for the planned data types and remote
procedures.
4. Use the DCE IDL compiler to generate the client and server stubs. (The IDL
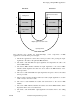
compiler can invoke the C compiler to create the stub object code.) Figure 11-4
illustrates this task.
Figure 11-4. Generating Stubs
Server
stub
Client
stub
IDL Compiler
Interface
definition
file
Note: Optionally, instead of generating stub object code (which is not
portable), the IDL compiler can generate the stubs as ANSI C
compliant source code.
5. Write or modify application code by using a compatible programming language;
that is, a language that can be linked with C and can invoke C procedures, so the
application code works with the stubs.
Application code includes several kinds of code, as follows:
a. Remote procedure calls
b. Remote procedure implementations
c. Initialization code (calls to RPC stub-support or runtime routines)
d. Any non-RPC code your application requires
11 − 8 Tandem Computers Incorporated 124245