OSF DCE Application Development Guide--Core Components
DCE Application Messaging
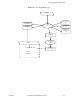
it. If the message catalog is inaccessible, and the message exists in an
in-memory table, then this message (the default message) is returned in
the allocated space. If neither the catalog nor the default message is
available, an error status code is placed in the status output parameter.
The following code fragment shows how dce_msg_get_msg( ) might be
called to retrieve the ‘‘Hello World’’ message defined in the example
program earlier in this chapter:
#include <dce/dce.h>
#include <dce/dce_msg.h>
#include "dcehelmsg.h"
unsigned char *my_msg;
unsigned32 status;
<. . .>
my_msg = dce_msg_get_msg(hello_msg, &status);
printf("Message is: %s\n", my_msg);
free(my_msg);
dce_msg_get()
This is a convenience form of dce_msg_get_msg(). If it fails, it does not
pass back or return a status code, but instead fails with an assertion error,
that is, aborts the calling process.
The following code fragment shows how the routine might be called to
retrieve the ‘‘Hello World’’ message defined in the example program
earlier in this chapter:
#include <dce/dce.h>
#include <dce/dce_msg.h>
#include "dcehelmsg.h"
unsigned char *my_msg;
<. . .>
my_msg = dce_msg_get(hello_msg);
printf("Message is: %s\n", my_msg);
free(my_msg);
dce_msg_get_default_msg( )
Retrieves a message (identified by a global message ID) from an in-
memory message table and returns a pointer to static space containing
the message retrieved. If the default message is not available, an error
status code is placed in the status output parameter.
The following code fragment shows how dce_msg_get_default_msg( )
might be called to retrieve the in-memory copy of the ‘‘Hello World’’
message defined in the example program earlier in this chapter:
124245 Tandem Computers Incorporated 3− 13