OSI/FTAM and OSI/APLMGR SCF Reference Manual
Introduction to SCF for Tandem FTAM
OSI/FTAM and OSI/APLMGR SCF Reference Manual—421943-001
1-3
OSI/APLMGR and OSI/FTAM Subsystems
Role of APLMGR Subsystem
The APLMGR subsystem manages the Tandem FTAM Application Layer components—
that is, the initiator and responder processes. The APLMGR subsystem consists of the
APLMGR process and the management information base (MIB), a key-sequenced
Enscribe file that stores the configuration information for the APLMGR, initiator, and
responder processes. The APLMGR process uses the information stored in the MIB to
create the initiator and responder processes. The APLMGR process can then start, stop,
suspend, activate, and abort these processes.
Role of FTAM Subsystem
The Tandem FTAM subsystem consists of the initiator and responder processes. The
initiator process allows a user to send requests to remote responders on an OSI network.
Once an association is made, the initiator allows you to use the services of a remote
FTAM responder.
The responder process receives and fulfills requests from a remote FTAM initiator. It
performs mapping between Guardian file structures and FTAM file structures, and
between Guardian file operations and FTAM requests.
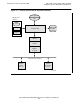
Roles of Underlying Subsystems
To communicate over OSI networks, Tandem FTAM uses the services of the Tandem
Open Systems Interconnection/Application Services (OSI/AS) and the OSI/Transport
Services (OSI/TS) subsystems, along with (depending on the configuration) one or more
of the following communications subsystem:
•
Tandem Local Area Network (LAN) Access Method, or TLAM [replaced by the
Port Access Method (PAM) for G-series systems]
•
X.25 Access Method (X25AM)
•
Tandem NonStop TCP/IP
Figure 1-1
on page 1-4 shows how these products are related to Tandem FTAM.