OSI/FTAM Programming Guide
NonStop FTAM Programming Examples
HP NonStop OSI/FTAM Programming Guide—528612-001
5-2
Sample Program Structure
•
How to operate on a more complex document type (FTAM-2) and perform more
complex file operations (such as file updates)
•
How to use nowait mode
•
How to maintain multiple active associations
Each example in the OSI/FTAM Programming Reference Manual is provided in both C
and TAL.
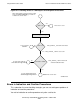
Sample Program Structure
The examples excreaf3 (read an FTAM-3 file) and extwrif1 (write an FTAM-1 file),
although functionally different and written in different programming languages, have
almost exactly the same structure. Each consists of these parts and routines, defined
and nested to match the FTAM regime hierarchy. (The spelling of the names differs
slightly in C and TAL.)
•
Compiler directives and global declarations incorporate the FTAM API and various
Guardian procedures and data structures into the program, and define a variety of
variables and constant values that the program will use.
•
main initializes a segment for use by the FTAM API, creates a local file (in the read
example) or opens one (in the write example), and calls another routine to enter
the FTAM regime. The TAL example also includes standard code for managing the
terminal and reading the Guardian startup message.
•
ftam_regime initializes parameters for an association, requests the association and
ultimately terminates it, in the meantime calling another procedure to enter the
file-selection regime.
•
file_selection_open_regime creates and opens a remote file (in the write example)
or opens an existing remote file (in the read example). It calls another routine to
enter the data-transfer regime, and, when that call has completed, it closes the
remote file.
•
data_transfer_regime accomplishes the data transfer, using a combination of
FTAM and Guardian procedure calls.
•
get_event is called by other routines to find out whether an expected event (such
as a confirm or indication) has occurred.
•
bad_event deallocates the segment and stops the program if an unexpected event
has occurred.
•
check_action displays an error message if a call has a bad action result, and calls
another routine to retrieve diagnostic information.
•
check_diag checks for diagnostic information, displays a message, deallocates the
segment, and stops the program.