OSI/MHS Configuration and Management Manual
Introduction to OSI/MHS
OSI/MHS Configuration and Management Manual—424827-003
1-3
OSI/MHS
The remainder of this section describes OSI/MHS.
OSI/MHS
OSI/MHS is a powerful store-and-forward messaging subsystem that provides you with
access to the X.400 network and allows you to implement such services as funds
transfer, ordering, billing, and large-scale electronic-mail connectivity.
OSI/MHS provides the following functions:
•
Serves as a message transfer agent between adjacent MTAs
•
Provides access to the X.400 network for Transfer users through a Transfer X400
gateway
•
Provides access to proprietary systems through a general user gateway (GPI)
•
Provides message submission and message-store capabilities for UAs
•
Provides interfaces for remote and local UAs to access the message store
•
Records information useful for accounting and message tracking, such as:
•
Submissions, deliveries, and relays of messages through the subsystem
•
Storage of messages within OSI/MHS
•
Registration of users and adjacent MTAs
•
Provides management and administrative functions using the Distributed Systems
Management (DSM) mechanisms and tools
Architecture
Each OSI/MHS subsystem operates as an X.400 message transfer service, message-
store service, and/or remote operations service. As a message transfer service, each
OSI/MHS subsystem can interoperate with other OSI/MHS MTAs and MTAs on other
systems. As a message store, it can interoperate with various remote and local UAs.
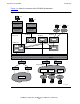
Figure 1-2 shows an overview of a OSI/MHS subsystem. Each two-letter abbreviation
on the figure represents a group of one or more processes that perform a specific
function in OSI/MHS:
•
MR (message relay) groups provide the MTA function.
•
RS (remote operations service) groups support remote user agents.
•
GI (gateway interface) groups provide connection with other messaging systems.
•
LO (local operations service) groups support local user agents.
•
MS (message store) groups provide long-term storage of messages.
Each of these groups is described in more detail later in this section.