OSI/MHS Configuration and Management Manual
Introduction to OSI/MHS
OSI/MHS Configuration and Management Manual—424827-003
1-8
Roles of OSI/MHS
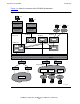
The Transfer X400 gateway, which is described later in this section, provides access to
the X.400 network for Transfer applications, such as PS Mail. You can use PS Mail to
transfer messages to an X.400 recipient defined as an MS user on OSI/MHS or to an
adjacent MTA for external delivery. Likewise, you can receive X.400 messages through
your PS Mail application.
The Gateway Programmatic Interface (GPI) lets you develop a client application that
provides users of your proprietary system with access to the X.400 network through
OSI/MHS. GPI consists of a library of procedures and a service that implements these
procedures. For more information, see the OSI/MHS Gateway Programmatic Interface
(GPI) Reference Manual and the OSI/MHS Gateway Programmatic Interface (GPI)
Programming Guide.
Using OSI/MHS as a Message Store
OSI/MHS can provide mailboxes in message stores for access by UAs. Figure 1-6
shows this implementation.
Figure 1-5. Gateway Function of OSI/MHS
Note. In this manual, the term mailbox means a message store as defined by X.400.
006VST .VSD
NonStop System
X.400
Network
Transfer
Mail
Transfer
X400
Gateway
MTA
OSI/MHS
Proprietary
System
GPI