OSI/MHS Configuration and Management Manual
Routing in OSI/MHS
OSI/MHS Configuration and Management Manual—424827-003
E-3
Basic Routing Components and Logic
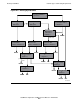
In Figure E-1 there are three routes from MTA 1:
•
Route 1 is for users on a different MTA but still part of the same PRMD. In this
situation, additional routing criteria (such as organization name, organizational unit
name, or domain-defined attributes) are required.
The O/R name elements for route 1 are as follows:
•
Route 2 is for recipients in a different domain within the same country as the MTA.
The route is defined with the country and administration domain name only. The
O/R name elements for route 2 are as follows:
•
Route 3 is for recipients in a different country. We could designate that route by
specifying the country name. Alternatively, we could define a “catch-all route,”
specifying that all messages addressed to recipients in other countries or domains
be routed to a specific adjacent MTA. The O/R name elements for route 3 are as
follows:
When users are defined for a gateway or message store, these too must have routes,
which you define using the APPL object. The routing action results in delivery of
messages to those users (who are considered local in that they are served by the MTA
doing the routing). This factor adds complexity to the routing algorithm. Another
feature is support for distribution lists. A distribution list is also considered a point of
delivery.
Basic Routing Components and Logic
The routing function of OSI/MHS is implemented in three major components:
•
The routing database
•
The routing table
•
The routing algorithm
The routing database contains the routes defined for the subsystem (through SCF or
a management application). This database is maintained by the MHSMGR process,
and any time a ROUTE, APPL, or DLIST object is defined, an entry is made in the
database. The only other OSI/MHS processes that update the database are the MS
processes, which update only the logged-on state of APPL objects.
Country name (C)
ADMD (A)
PRMD (P)
Organization (O)
Country name (C)
ADMD (A)
none (catch-all)