OSI/MHS Gateway Programmatic Interface (GPI) Programming Guide
Recovering From Errors
OSI/MHS Gateway Programmatic Interface (GPI) Programming Guide—424822-001
6-10
Information Buffer
If total-info-length exceeds info-buffer-length, the error information
is truncated. To read all the available information, you must call GPI_STATUS_ again,
this time with a value of info-buffer-length that matches or exceeds total-
info-length.
Types of Buffer Structures
Information returned to the buffer is contained in data structures of five formats.
Depending on the error, different combinations of the five structures are returned. Note
that the structures might be returned in any order.
Figure 6-4 shows a buffer that contains all five types of structures. The structures are
labeled with their DDL names: ZGPI-INFO-1, ZGPI-INFO-2, ZGPI-INFO-3, and so
on. Note that for purposes of this example, all five structures are shown the same size.
However, structure types actually vary in size.
In this example, the structure ZGPI-INFO-1 is resolved into its second-level
components: ZGPI-ST-ATTR-DATA, its 32-bit identifier, and ZGPI-ERROR-ATTR-
DATA, a subordinate structure that contains error data. ZGPI-ERROR-ATTR-DATA is
further resolved into its individual error fields.
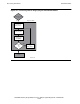
Figure 6-3. Information Buffer Parameters
Note. It might be useful to call GPI_STATUS_ initially with a value of zero for info-buffer-
length. When GPI_STATUS_ returns total-info-length, you can initialize info-
buffer-length to that value and repeat the procedure call.
603CDT .CDD
Error Information
actual_info_length
total_info_length
Information Buffer
info_buffer_length
info_buffer
pointer