OSI/MHS Management Programming Manual
Password Server Interfaces
OSI/MHS Management Programming Manual—424824-001
7-28
Alternative MPS Configurations
•
Creation of a database file
•
Inconsistency in configuration information
•
Errors in opening or writing to database files
•
Fatal errors requiring termination of a server
A complete list of MPS errors and informational messages appears under the heading
MPS Error and Informational Messages
on page 7-45.
MS Bind Password Server Interface
The MPS uses the MS bind password server interface described in MS Password Server
Programmatic Interface on page 7-8. That is, the MPS uses SPI messages and related
protocols to receive and respond to requests from MS processes (in the case of MS Bind
requests and Register-MS requests to change a user’s password) and the MHSMGR (in
the case of ADD, ALTER, and DELETE requests affecting an APPL object).
The use of any password server supplements the normal validation functions of the
MHSMGR process. If you specify use of a password server, the MHSMGR process
ensures that an ADD, ALTER, or DELETE request is authorized (in the sense that the
requester is permitted to issue sensitive commands) and appeals to the password server
to perform additional validation. Although the Master Password Server does not
validate passwords in such cases, you can modify it to do so or to perform other
validation functions.
PATHMON or TACL
You can use either PATHCOM or a TACL command interpreter to run and manage the
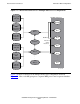
MPS. Figure 7-3 shows PATHMON, the monitor process in the Pathway environment.
PATHCOM is the interactive interface to PATHMON.
If you use PATHCOM, Pathway stores the configuration information for your MPS
processes and automatically restarts a server if it fails. An MPS process is defined as a
server class consisting of one static server: Pathway will not dynamically create new
instances of an MPS as workload increases.
If you use a TACL command interpreter, you must manually restart a failed server or,
more likely, run a script to restart it.
The TACL language is a standard product on the NonStop system. Pathway is not
routinely supplied with OSI/MHS or the MPS.
Alternative MPS Configurations
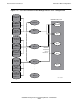
In the configuration illustrated in Figure 7-3, one MPS process performed authentication
services for all the MS groups in the OSI/MHS subsystem. Figure 7-4, Figure 7-5, and
Figure 7-6 show other configurations, in which different MPS processes and potentially
different master users are assigned to different MS groups.