PAM Configuration and Management Manual
Introduction
PAM Configuration and Management Manual—523349-003
2-4
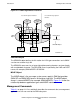
The PAM Subsystem’s Role Within the System
Management Interfaces
The PAM management interfaces consist of the Subsystem Control Facility (SCF) and
SPI. SCF provides an interactive interface for control-and-inquiry and accesses the
PAM subsystem through SPI.
SPI transfers SCF commands to the PAM subsystem and also provides an interface for
writing management applications that perform control-and-inquiry and event
management.
For information about how to write management applications that use SPI, see the
PAM Management Programming Manual.
ServerNet LAN Systems Access (SLSA) Subsystem
PAM uses the SLSA subsystem to access the Ethernet and token-ring LANs attached
to the NonStop S-series server and the Integrity NonStop NS-series server. SLSA has
a logical interface (LIF) that is the point-of-connection to SLSA for I/O clients (such as
PAM).
Logical Interface (LIF)
The LIF in the SLSA subsystem corresponds to the LIF on the adapter and, therefore,
to one of the Ethernet or token-ring LANs attached to the system.
QIO Shared Memory Segment
The QIO subsystem performs efficient I/O by allowing client processes to transfer data
directly to the QIO shared memory segment and to pass a pointer to the location so
that the actual data does not need to be moved again.
PAM Process
The PAM process provides the interface to the SLSA subsystem for Ethernet, LLC1
and LLC2 applications, SNAX/XF and SNAX/APN, and EMS.
Event Management Service (EMS) makes event messages generated by the PAM
process available to management applications. EMS collects, logs, and distributes
event messages that provide information to help you monitor the network environment,
analyze failures, and recognize and handle critical problems. Figure 2-2
on page 2-5
shows how EMS manages events.