Pathway/iTS TCP and Terminal Programming Guide
Introduction to TCP and Terminal Application
Programming
Compaq NonStop™ Pathway/iTS TCP and Terminal Programming Guide—426751-001
1-16
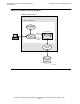
Transaction From an Intelligent Device
3. The workstation application checks the input data, confirming that the account
number entered has no more than seven characters. The workstation application
then displays a new screen showing the customer information as it is currently
recorded in the database.
4. The clerk enters the new information (for example, a new customer telephone
number) in the appropriate field and requests that the information be updated by
pressing a function key.
5. The requester checks the input data for validity and confirms that there are no input
errors.
6. The workstation application formats a request message containing the name of the
server class and the data needed by the server to complete its work. The workstation
application—with the aid of user-developed conversion procedures—converts its
data to SCREEN COBOL format, a representation acceptable to the TCP.
7. The workstation application executes a SEND statement, directing the request
message to be sent to the specified server class. A user-developed communications
subsystem forwards the request to the TCP using a supported protocol. The IDS
requester, which is the TCP interpreting a SCREEN COBOL program, receives the
request message as part of an IDS SEND MESSAGE statement. The TMF
transaction begins.
8. If the TCP does not have a link to the specified server class, the TCP asks the
PATHMON process for a link to a server process in the server class. The
PATHMON process replies that a server process is available. If the TCP already
has a link to the server class, this step is not performed.
9. The TCP forwards the request to the server process by using the interproces
communication mechanism of the NonStop™ Kernel operating system.
10. The server process receives and reads the request message.
11. Executing NonStop™ SQL/MP statements in its program, the server process
accesses the database, using the account number as the key, and updates the
specified customer information.
12. The server process formats a reply message verifying the database update and
replies to the TCP using the interproces communication mechanism of the
NonStop™ Kernel operating system.
13. The TCP receives, interprets, and then forwards the reply message to TERM-1 using
the IDS SEND MESSAGE statement. The TMF transaction ends.
14. The workstation application displays a message on the workstation screen verifying
that the specified information has been updated.