RDF/IMP and IMPX System Management Manual (RDF 1.3+)
Introducing RDF
Compaq NonStop™ RDF/IMP and IMPX System Management Manual—522204-001
1-12
Monitor Process
Monitor Process
The monitor process is a process pair that normally runs on the primary system. This
process is responsible for starting, stopping, and monitoring all other RDF processes on
the primary and backup systems.
On the primary system, you can either name the monitor process explicitly (by issuing a
SET MONITOR PROCESS command) or have the Compaq NonStop™ Kernel
operating system name it for you (a name such as $Xnnn, $Ynnn, or $Znnn, where
nnn is a three-digit number). If a monitor process needs to be started on the backup
system during an RDF takeover, the operating system names it.
Extractor Process
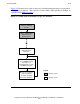
An extractor process is a process pair that runs on the primary system. Each extractor
process reads an audit trail (the MAT or a particular auxiliary audit trail), filters out audit
records not relevant to the backup database, and then transmits the relevant audit records
over the Expand network to an associated receiver process on the backup system, as
shown in Figure 1-4.
Reading large amounts of data from the MAT, the extractor process stores the following
records for subsequent transmission to the backup system:
•
All transaction state records
•
TMP control point records
•
Records generated by the TMF backout process
•
Audit records associated with volumes protected by RDF
•
For Enscribe files (DDL operations) only, the following file-label modification
records:
CREATE
PURGEDATA
ALTER MAXEXTENTS
•
Stop-RDF-Updater records
•
TMF shutdown records
The extractor filters out all other records and does not send them to the receiver. Among
those filtered out are audit records for volumes not protected by RDF and most of the
physical audit records generated either for block splits or during FUP RELOAD
operations.
The extractor always tries to fill the buffer to be sent to the receiver. The buffer never
contains partial records; if the buffer is nearly full and the next record to be transmitted
does not fit in its entirety, the extractor transmits the current buffer and puts the record at
Note. The discussion and figure that follow are both oriented to the extractor associated with
the MAT. For information about protecting auxiliary audit trails, see Section 12, Auxiliary Audit
Trai ls.