RDF/IMP and IMPX System Management Manual (RDF 1.3+)
Introducing RDF
Compaq NonStop™ RDF/IMP and IMPX System Management Manual—522204-001
1-14
Receiver Process
Although the extractor runs as a process pair, the primary process does not maintain
restart information nor checkpoint this information to its backup. Instead, the receiver
maintains all restart information for the extractor, ensuring that the extractor is
restartable. The restart point is based on the MAT position of the last record safely
stored in the image trail on the backup system.
Whenever you start RDF, the extractor requests its starting position in the MAT from the
receiver. Because this position is based on the MAT position of the last image record
safely stored in the image trail by the receiver, this method guarantees that no audit is
mistakenly omitted. If the primary extractor process fails, the backup process requests
from the receiver a new starting position in the MAT, further guaranteeing a correct
restart position. This extractor-receiver protocol also provides protection against
messages from the extractor erroneously arriving out-of-order: if a message arrives out-
of-order, the receiver directs the extractor to restart.
When it reads from an audit trail file, the extractor pins the file by sending a message to
TMF. Once pinned, an audit trail file remains pinned until the extractor unpins it or you
issue the following RDFCOM command at the primary system:
UNPINAUDIT
If you unpin files, RDF cannot be restarted if the files required by the extractor cannot
be made available. When you unpin audit trail files, be sure that these files are dumped
to disk or tape. If they are not dumped, and the TMP renames the file or files required by
the extractor, you will have to reinitialize RDF and resynchronize the primary and
backup databases.
In response to the UNPINAUDIT command, RDFCOM issues a prompt asking you to
confirm your request.
If the files are unpinned successfully, RDFCOM issues an informational message to that
effect.
If an error occurs while attempting to unpin the audit trail files, the command is ignored,
and RDFCOM issues a message indicating the error.
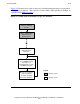
Receiver Process
A receiver process is a process pair that runs on the backup system. There is one receiver
for each configured extractor. A receiver process accepts audit records from its extractor,
sorts them, and then writes them to the appropriate RDF image trail, as shown in
Figure 1-5. (The restartability of a receiver ensures the receiver's correctness at process
takeover or under any conditions requiring resynchronization with its extractor.)
A receiver determines which updater will apply the data, and sorts the data into the
image trail used by that updater. The records in the image trails are subsequently used by
updater processes to update the backup database.
Each receiver also creates image trail files, preallocates extents, and initiates rollovers.