RDF/IMP, IMPX, and ZLT System Management Manual
Introducing RDF
HP NonStop RDF/IMP, IMPX, and ZLT System Management Manual—524388-002
1-14
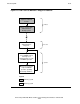
Primary System Processes
Primary System Processes
On the primary system:
•
The monitor process coordinates subsystem starts and stops, some messages,
and NonStop SQL/MP DDL operations using the WITH SHARED ACCESS option
on protected volumes, and monitors the other RDF processes.
•
Each extractor process reads an audit trail (the MAT or a particular auxiliary audit
trail), filters out audit records not relevant to the backup database, and then
transmits the relevant audit records to an associated receiver process on the
backup system. Some control information for synchronizing the extractor and
receiver process pair is included each time the extractor process transmits the
audit records.
Backup System Processes
On the backup system:
•
There is one receiver process for each configured extractor process. A receiver
accepts the audit records from its extractor, sorts them, and then writes them to the
appropriate RDF image trail.
•
There is one updater process for each primary system volume being protected by
RDF. Updater processes read image records from their RDF image trails and pass
the transaction records to the disk process so that the disk process can perform
the logical REDO operations. The backup database is updated in cache each time
the disk process performs a logical REDO operation requested by an updater
process.
•
The purger process interacts with the updaters to determine when image files can
be purged, and also determines which transactions updaters must undo for
takeover and stop-update-to-time operations.
ZLT Standby System Process
The audit-fixup process is one of several processes that run on the remote standby
system only in a ZLT configuration at takeover time. It repairs CRASHOPEN audit-trail
files the extractor(s) on the remote standby system need to read. For information on
ZLT processing, see Section 16, Zero Lost Transactions (ZLT).
RDF Operations
RDF can be run with updating of the backup database either enabled or disabled.
When updating is enabled, the RDF processes maintain a current, online copy of the
primary database on the backup system. By default, the subsystem starts with
updating enabled, and the RDF processes continue their updating activities until
updating is explicitly disabled or the subsystem is shut down.