RSC/MP 7.2 Programming Manual
API Functions and Options
HP NonStop Remote Server Call (RSC/MP) Programming Manual—522360-004
3-6
Connecting to the TDP
Connecting to the TDP
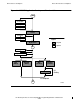
An RSC/MP connection opens a communications channel between your application
and the TDP. Establishing a connection ensures that a physical path exists between
the workstation and the host system. All application instances that use RSC/MP must
issue a call to the RscConnect function. The RscConnect function returns a connection
handle for use with other RSC/MP functions. Use the RscDisconnect function to close
the connection and free all resources associated with the connection (session, I/Os,
and so on).
Beginning and Ending Sessions
Begin and end sessions by using the RscBeginSession and RscEndSession function
calls. An RSC/MP session provides a context for I/O, transaction control, and the
Unsolicited Message Service (UMS). To use any of these services, an RSC/MP
connection must have at least one session.
Beginning and Ending Transactions
Use only one TMF transaction for each session. Use the RscBeginTransaction function
to start the transaction and the RscEndTransaction to end (or commit) the transaction.
The RscAbortTransaction function aborts (or rolls back) the outstanding transaction. If
the outstanding transaction is aborted, the updates associated with the transaction
started by the session’s RscBeginTransaction function call are rolled back to their
original status in the database.
An alternative method of controlling transactions is described under Generating
Transactions Automatically (Implicitly) on page 6-8.
See Monitoring Transaction Calls on page 6-6 for information about using TMF, starting
transactions, and a TMF code example.
Processing I/O Using Waited and Nowaited
Calls
Use the RscWrite, and RscWriteRead I/O functions to write and read from a remote
process. The RscIoCheck function checks for completion of nowaited I/O.
When writing your application, determine whether you want to use waited calls that
pause the workstation application until the I/O is completed and then return a reply; or
nowaited calls that do not wait for the I/O to complete and allow you to continue
processing. See Waited and Nowaited I/O on page 5-3 for more information on waited
and nowaited I/O.