SCF Reference Manual for the Storage Subsystem (G06.24+, H06.03+)
Disk Load Balancing
SCF Reference Manual for the Storage Subsystem—529937-007
8-11
PRIMARY Command Function in G05.00 and Earlier
$D0203 also changes primary processors in because:
1. The disk process executing in processor 2 attempts to access $D0203-P.
The path to $D0203-P on the X fabric leads through SAC 2. Because of the
PRIMARY command on the other disk, this SAC is now owned by processor 3.
Because the disk process is executing in processor 2, the disk access fails.
2. The disk process detects the loss of SAC ownership, changes processors, and
tries to access $D0203 through processor 3. Because this SAC is now owned by
processor 3, the disk access succeeds.
3. The disk process, now executing in processor 3, attempts to access $D0203-M.
The path to $D0203-M on the Y fabric leads through SAC 1. Because this SAC is
also owned by processor 3, the disk access succeeds.
This process affects all disk processes that use these SACs.
PRIMARY Command Function in G05.00 and Earlier
On G05.00 and earlier RVUs, the PRIMARY command changes SAC ownership.
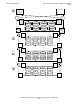
1. Before the PRIMARY command is issued, the status of $D0203 is:
In the figures that follow:
•
SACs owned by processor 2 are shaded.
•
Disk processes that are primaried in processor 2 are shaded.
•
Primary paths are the bold lines.
•
Backup disk processes are represented with a prime mark, such as $D0201'.
Note. When ownership of both SACs is lost, a read from one or both paths detects a loss of
ownership. However, a read from one path whose SAC ownership was not lost would not
detect the loss of ownership of the SAC on the path to the other disk.
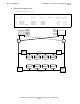
STORAGE - Status DISK \WAGER.$D0203-*
LDev Path Status State Substate Primary Backup
PID PID
105 PRIMARY ACTIVE STARTED 2,22 3,16
105 BACKUP INACTIVE STARTED 2,22 3,16
105 MIRROR ACTIVE STARTED 2,22 3,16
105 MIRROR-BACKUP INACTIVE STARTED 2,22 3,16