SNAX/APC Application Programming Manual
Using the Application Program Interface
SNAX/APC Application Programming Manual—138786
1-23
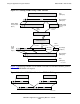
Parsing SNAX/APC Reply Messages
Any violation of conversation states will result in immediate deallocation of the
conversation.
Parsing SNAX/APC Reply Messages
When you receive a reply to a SNAX/APC request (a service UOW, a control operator
verb, or a conversational verb), the following steps are recommended to ensure that the
request completed correctly:
1. Check the REPLY-CODE field in the IPC reply header:
°
If the reply header equals ALL-UOWS-OK, go to Step 2.
°
If the reply header is not equal to ALL-UOWS-OK, the reply code indicates the
source of the error. UOWS-WITH-ERROR indicates that one of the UOWs in
the IPC message caused an error. REQUEST-ERROR indicates that an error
was detected in the request; no UOW replies are returned. If the TP receives
REQUEST-ERROR, the TP must check the IPC HEADER-RETURN-CODE
field for further information. Some of the HEADER-RETURN-CODE fields
also have HEADER-RETURN-CODE-DETAIL values (INVALID-UOW-
HEADER, INVALID-RESOURCE-ID, and SERVICE-DENIED).
°
If REPLY-CODE contained UOWS-WITH-ERROR and the IPC message
contained more than one UOW, the value in the UOWS-OUT field indicates the
UOW that caused the error. For example, if UOWS-OUT contains the value 3, it
means that SNAX/APC processed two verbs successfully, but that the third verb
caused an error. Proceed with Step 2.
2. Examine the UOW headers in the order in which they occurred in the IPC request
message. Examine the contents of REPLY-RETURN-CODE:
°
If REPLY-RETURN-CODE contains RC-OK or RC-DEALLOCATE-
NORMAL, the UOW completed successfully.
°
If REPLY-RETURN-CODE contains any other return code, the TP should use
the return code and detail fields to determine the source of error.
Once these steps are completed, you may continue processing.
RECEIVE-AND-WAIT Processing
Most TPs perform more complex functions than simply allocating a conversation,
sending data, and deallocating the conversation. Any TP that performs more than this
must prepare to receive information from the SNAX/APC server. This information
includes state changes, requested attribute information, or data from the remote TP.
Note that the discussion in this subsection assumes that the people writing TPs on either
side of the conversation have established conventions for transactions. When a TP
enters a conversation, it should be understood who terminates the conversation (under
Note. A simple check for RC-OK is not sufficient; RC-DEALLOCATE-
NORMAL is not an error return code. (RC-DEALLOCATE-NORMAL can be
returned from either RECEIVE-AND-WAIT or SEND-ERROR).