SNAX/APN Application Programming Manual
The SNALU Interface
SNAX/APN Application Programming Manual—420111-001
4-4
SNAX Header
TC Indicators
The application and the SNAX/APN line handler share the SNA transmission control
functions. Bytes 0 and 1 of the SNAX header are used for passing certain TC indicators
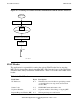
back and forth between the two processes. Figure 4-3 shows the format of the TC
indicators field.
Queue Request Indicator
QRI is the Queue Request Indicator, where
•
0 not a queue control request.
•
1 queue control request.
If this bit is set by the application when initiating a read operation, the resulting read
operation completes with a byte count in the data portion of the application I/O buffer.
The PLU or SLU then initiates another read operation specifying the returned count as
read-count. This is analogous to the two-step read operation used by other access
methods. Only one QRI read request can be pending at any given time. For more
information about the use of this control bit, see Two-Step Read Operations (QRI
Usage) on page 4-7.
Expedited Flow Indicator
EFI is the Expedited Flow Indicator, where
•
0 RU is a normal-flow RU (such as INIT-SELF, application data, CINIT,
TERM-SELF, and character-coded logon or logoff).
•
1 RU is an expedited-flow RU (such as BIND, CLEAR, STSN, and UNBIND).
For more information about normal and expedited flow, see Normal/Expedited Flows
on
page 4-18.
Logical Unit Network Services (LUNS) Indicator
LUNS is the Logical Unit Network Services indicator, where:
•
0 BIU is destined for or being received from the remote LU.
•
1 BIU is destined for or being received from a SNAX/APN logon manager
(TLOGMGR).
Figure 4-3. TC Indicators in a SNAX Header
403CDT .CDD
Byte 0 Byte 1
(Reserved) QRI EFI
Bits: 0 - 5 6 7 8
9 - 15
(Reserved)LUNS