SNAX/XF and SNAX/APN Configuration and Management Manual
Configuring for Token-Ring Support
SNAX/XF and SNAX/APN Configuration and Management Manual—425836-006
9-12
SAPs and Link Station Addresses
SAPs and Link Station Addresses
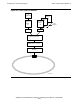
In Token-Ring architecture (and other 802 access methods), service access points
(SAPs) are the interfaces between the LLC layer and the user application in the upper
layers, as shown in Figure 9-8 on page 9-13. Each SAP provides services related to
the type of protocol stack it supports, identifying the client layer to the lower layers and
indicating the format of the data passed between the layers.
Each SAP is identified by a hexadecimal SAP value. The SAP value typically identifies
to the receiving station what format the data portion of the frame is in. For example,
SAP value %H04 is considered an SNA Path Control individual SAP. This means that
the data is an SNA path information unit (PIU). Other SAP values have other
meanings; see Table 7-1 for example values.
The important point to note from the table is that the SAP values indicating that the
data is an SNA PIU are always multiples of four. You may choose to use any of these
permissible values (X’04’, X’08’, X’0C’, and so on) with the SAPINFO parameter when
configuring SNAX/APN.
Each device attached to the ring can have one or more SAPs, with each SAP
supporting a different protocol stack. For example, in Figure 9-8 on page 9-13 you can
see SAP 1 and SAP 2 both associated with a single device on the ring, and each
supporting different protocols. Each SAP may support multiple applications all using
the same protocol; for example, protocol stack #2 demonstrates the support of three
separate link station addresses.
The term “link station address” is used to describe the unique combination of SAP (with
associated data link services) and the MAC address of the device. It is the functional
equivalent of a PU address in SNA terminology. There is one link station at each end of
a connection on the ring, just as there is one PU at each end of a traditional SDLC line.
Table 9-1. Architected LLC Service Access Points
HEX Definition Description
X’04’,
X’08’,
X’0C’ and so on.
SNA path control SAPs Used by SNA workstations and supported by
SNAX/APN.
X’05’ Path control group SAP A broadcast address to all SNA SAPs. (Not
supported by SNAX/APN.)