SNMP Configuration and Management Manual
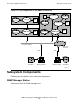
The NonStop SNMP Environment
SNMP Configuration and Management Manual—424777-006
1-9
Information Protocol
Also, all agents can interpret information encoded according to the basic encoding
rules (BER) associated with ASN.1, which define how to encode an ASN.1 value as an
octet string. BER-encoded packets can be transmitted over any transport protocol that
the manager and target agent mutually support.
Transmission Protocols Supported by the SNMP Agent
IPC-encoded SNMP packets are transmitted and received through NonStop Kernel
interprocess communication calls. The SNMP agent supports the interface, #MGR,
through which an IPC communication path between an SNMP manager and a SNMP
agent can be established.
The most widely supported transmission protocol for transmitting and receiving BER-
encoded SNMP packets is TCP/IP’s User Datagram Protocol (UDP). The SNMP agent
supports the UDP protocol.
Differences in the way the SNMP agent handles requests received through the HP
NonStop Kernel IPC and requests received through the UDP protocol are discussed
Section 2, Installing and Configuring the SNMP Agent and in Section 3, MIBs
Supported by the SNMP Agent.
Information Protocol
The foundation of any network management system is a collection of information about
the elements to be managed. In SNMP environments, this information is described by
a MIB (Management Information Base). Each item in a MIB is known as a MIB object.
•
Internet-standard MIBs. These MIBs are approved by the Internet Architecture
Board (IAB). MIB-I, MIB-II, and Remote Network Monitoring MIB. MIB-I is the
original MIB for managing TCP/IP-based internets. MIB-II is an extended version of
MIB-I and provides additional object definitions. Remote Network Monitoring MIB
defines objects that manage remote network monitoring devices. Most MIB-II
objects are supported by the TCP/IP Subagent; two MIB-II groups (System and
SNMP) are supported by the SNMP agent. The Host Resources Subagent
supports the standard Host Resources MIB, which is contained in the MIB-II
subtree.
•
Experimental MIBs. These MIBs are used in Internet experiments.
•
Enterprise MIBs. These MIBs are vendor defined.
To promote interoperability, SNMP defines a standard scheme for naming all MIB
objects.