SNMP Configuration and Management Manual
The NonStop SNMP Environment
SNMP Configuration and Management Manual—424777-006
1-12
The Management Information Base
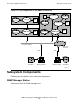
As Figure 1-4 indicates, MIB-II is described in the mgmt subtree. tandem has been
assigned the value 169 in the enterprises subtree. In the tandem subtree,
nonstopsystems has been assigned the number 3. The nonstopsystems subtree
contains MIBs and subsystems defined by HP.
In the zsmp subtree of the nonstopsystems node, the SNMP agent subtree,
zsmpagent, has been assigned the value 1. The object identifier for the SNMP agent
is:
1.3.6.1.4.1.169.3.155.1
In the zsmpagent subtree, the zagInternal group (value of 7), encompasses the four
subgroups (zagInProcess, zagInEndpoint, zagInProfile, and zagInTrapdest) that
constitute the private portion of the SNMP agent’s MIB. The object identifier for this
private MIB’s zagInternal group is:
1.3.6.1.4.1.169.3.155.1.7
Object identifiers not only identify organizations and their elements but also identify
MIB objects. For example, the zagInTdHostAddr object from the zagInTrapdest group
of the SNMP agent’s private MIB is:
1.3.6.1.4.1.169.3.155.1.7.4.2.1.4
The Management Information Base
Each MIB object is identified by an object descriptor and identifier. Sometimes MIB
objects are divided into groups called object groups. Most items subordinate to MIB-II
in Figure 1-4 are actually object groups. Examples are the UDP group, the Interfaces
group, and the TCP group. Many of these groups are supported by the TCP/IP
Subagent's MIB, as described in Section 8, TCP/IP Subagent.
Values for individual MIB objects can two forms:
•
Scalar. An object is assigned a scalar value when the object can have only one
value. The length of time since the SNMP subsystem was brought up (sysUpTime)
is an example of such an object.
•
Tabular. Some objects, such as TCP connections, can have multiple values, each
describing a single instance of the object. These object values are organized into
tables. Each row in the table represents information about a single object instance.
A row in a table is referred to as an entry.
Each MIB object has an access attribute. This attribute determines the kind of access
SNMP managers have to values of the object.
read-only The value can be retrieved but not modified.
read-write The value can be both retrieved and modified.
write-only The value can be modified but not retrieved.
not-accessible The value cannot be retrieved or modified.