SNMP Configuration and Management Manual
The NonStop SNMP Environment
SNMP Configuration and Management Manual—424777-006
1-14
Traps
Traps
Traps are unsolicited messages forwarded by an agent to SNMP managers when
significant events occur. Some traps and their contents are defined by the SNMP
standards. Other traps are proprietary. Traps that the SNMP agent supports are
defined in Part 3, MIBs Supported by the SNMP Agent. Traps that subagents offered
by HP generate are described in Part IV, SNMP Subagents.
The SNMP agent can be configured to send traps to one or more specific SNMP
managers. You can also suppress traps altogether.
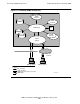
Architectural Overview of NonStop SNMP
Figure 1-5 illustrates how the SNMP agent interacts with NonStop system and network
elements to provide SNMP support:
•
The SNMP agent communicates with the remote SNMP managers through the
TCP/IP subsystem and these underlying subsystems:
°
X.25 Access Method (X25AM)
The X25AM subsystem supports WAN data communications over an X.25
packet-switching network and is supported on G-series and H-series RVUs of
the NonStop Kernel.
°
ServerNet LAN Systems Access (SLSA) subsystem
The SLSA subsystem supports parallel LAN I/O on systems that implement
ServerNet.
•
The SNMP agent authenticates requests as it receives them using the scheme
described in Section 2, Installing and Configuring the SNMP Agent.
•
The SNMP agent uses the Subsystem Programmatic Interface (SPI) protocol to
send event messages to an Event Management Service (EMS) collector. Refer to
Appendix C, Unsolicited SNMP Agent Messages
, for a description of event
messages originating from the SNMP agent and to Part IV, SNMP Subagents
for
events from subagents.
•
Most of the MIB-II groups are supported by the TCP/IP Subagent (see Section 8,
TCP/IP Subagent), which supports the management of TCP/IP resources. Two
MIB-II groups (System and SNMP) are supported by the SNMP agent. (See
Section 3, MIBs Supported by the SNMP Agent.)
•
The SNMP agent also supports a private MIB (zagInternal group) that describes
attributes of the SNMP agent process and defines the resources the SNMP agent
•
uses. These private MIB objects are defined by HP and are used to control the
configuration and operation of the SNMP agent.