SNMP Configuration and Management Manual
Installing and Configuring the SNMP Agent
SNMP Configuration and Management Manual—424777-006
2-20
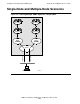
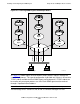
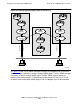
Single-Node and Multiple-Node Scenarios
In Figure 2-2, two SNMP agents are running on the same node. To run multiple agents
on a single node, issue the following two commands. Issue the first command from
one subvolume and the second command from a different subvolume.
•
From one subvolume:
RUN $SYSTEM.SYSTEM.SNMPAGT /NAME $ZSNM0, NOWAIT/
•
From a different subvolume:
RUN $SYSTEM.SYSTEM.SNMPAGT /NAME $ZSNM1, NOWAIT/
If the standard SNMP port for receiving requests is used (port 161), only one agent
process can use the TCP/IP subnet at a time. Distinct subnets ensure that each
message is routed to the appropriate target SNMP agent. Therefore, the type of
configuration illustrated in Figure 2-2 is possible only if at least one TCP/IP subnet is
available for each SNMP agent running. Each SNMP agent must be reached through a
separate Internet address. You can configure both NonStop TCP/IP and NonStop
TCP/IPv6 to have distinct subnets. (To configure distinct subnets for
NonStopTCP/IP/v6, use the Logical Network Partition feature described in the
TCP/IPv6 Configuration and Management Manual.)
In the Parallel Library TCP/IP environment, in order to bind each agent process to a
subnet, you must alter the ENDPOINT object and change the HOSTADDR attribute to
the IP address you want the agent bound to. See Remote Connections on page 2-37.
Caution. Each SNMP agent needs exclusive access to an SNMPCTL file. The SNMPCTL file
used is the file that resides in the subvolume from which the SNMP agent is started. Therefore,
each SNMP agent running on the same node must be started from the subvolume in which the
SNMPCTL file you want the agent to use resides.
Note. H-series RVUs do not provide support for Parallel Library TCP/IP.