SNMP Subagent Programmer's Guide
Programming Tutorials
SNMP Subagent Programmer’s Guide—119728 2-83
Security Checker
Logic
The logic for this subagent is contained in three files:
The main control block of Security Checker has the same structure as the main control
block of Nowaited Hello World, except for several added lines of code that provide
security checking before the program calls mgmt_poll().
Logic Flow
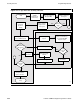
Figure 2-8 illustrates the logic flow of Security Checker; boxes with bold outlines
identify code that differs from the code for Nowaited Hello World. After initializing the
management environment and registering its MIB, the subagent initiates a nowaited read
from the NonStop agent. When an SNMP request arrives, mgmt_security() is called to
obtain the community string and host address of the manager station that sent the
request. The authentication function, authenticate(), parses the community string to
discover the subagent password, compare it with the password used at subagent
invocation, and set a flag indicating whether the password is valid or invalid.
When mgmt_poll() is called, the run-time library invokes the subagent’s access function
provided for the MIB object in the request. The access function checks the flag set by
authenticate() and processes the request only if the password is valid. If the operation
changes the value of helloPrintFreq, Security Checker sends a trap.
When connection with the agent is lost, the subagent terminates the management
environment and stops.
helloFreqChange TRAP-TYPE
ENTERPRISE hello
VARIABLES { helloPrintFreq }
DESCRIPTION
"A helloFreqChange trap signifies that the sending
hello world entity has had its `helloPrintFreq`
variable modified."
::= 0
END
EXTEND OBJECT-TYPE helloOutputText
WITH C_ACCESS_FUNC helloOutputText
IN C
EXTEND OBJECT-TYPE helloPrintFreq
WITH C_ACCESS_FUNC helloPrintFreq
IN C
EXTEND OBJECT-TYPE helloPrintCnt
WITH C_ACCESS_FUNC helloPrintCnt
IN C
helloscc The main control block
authentc The authentication function
securitc The access functions
Example 2-17. Security Checker MIB Definition (page 2 of 2)