SNMP Subagent Programmer's Guide
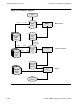
Subagent Development Cycle
1-8 119728—SNMP Subagent Programmer’s Guide
Introduction to Subagent Programming
This collection of functions offers a range of development strategies. Using only
management function calls to implement a subagent is the easiest and fastest approach,
because all the routines for MIB object handling are generated for you. When
optimizing your subagent warrants additional development time, you can write some
callback functions. And when more complete control over access logic is warranted,
you can write additional callback functions.
Refer to Section 4, “Writing Subagent Logic,” for more information on writing subagent
logic.
Refining the MIB
After you have decided how you want to represent MIB object values in your subagent
and whether you want to use callback functions, you add extensions to your MIB
definition. Extensions, constructs that are not part of the concise MIB constructs,
identify where in your subagent logic the values for MIB objects are maintained.
For example, the following MIB definition for an object named helloOutputText
contains an extension, highlighted in bold type, that indicates to the run-time library that
the value for the object is maintained in a global variable named helloText:
helloOutputText OBJECT-TYPE
SYNTAX DisplayString (SIZE (0..255))
ACCESS read-write
STATUS mandatory
DESCRIPTION
"The textual message that is displayed to stdout
by the Hello World program"
::= { hello 1 }
EXTEND OBJECT-TYPE helloOutputText
WITH C_VARIABLE helloText
IN C