SNMP Subagent Programmer's Guide
Dynamic Directory Program
2-48 119728—SNMP Subagent Programmer’s Guide
Programming Tutorials
Global Declarations
1. This subagent includes a file named errnoH, needed by the function named
next_file().
Main Control Block
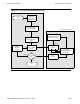
The main block controls the logic flow as indicated earlier in Figure 2-5:
2. The subvolume name is initialized to zsnmpsdk. This value can be changed by Set
operations from a manager.
3. The management environment is initialized.
4. The MIB is registered.
5. The table is registered. The second parameter, the address of
SMI_GROUP_fileEntry, identifies the location of the table entry structure. The
third parameter is a void pointer to the structure (defined in dirH) for the table.
Contrast this approach with individual row registrations, as performed by Static
Directory. When every row is registered, as in Static Directory, the third parameter
points to an individual entry, not to the whole table, and you provide no locator or
next functions for finding individual entries.
6. Incoming SNMP requests are processed until connection with the NonStop agent is
lost.
To process a Get or Set request, the run-time library uses locate_file() (14), the
locate function. This function builds the table, creating an entry for each file
currently associated with the most recently defined subvolume name. To build the
table, the locate function calls build_files() (15), which is defined in dirC (19); this
function calls insert_new_file(), also defined in dirC (18), to add entries to the table.
The function comp_files() is called (16) to identify whether an input file name
matches a name in the table; comp_files() is defined in dirC (17).
To process a GetNext request, the run-time library also uses locate_file(), but first
uses next_file() (8) to determine the index of the lexically next row. The next
function calls build_files() (9) to re-build the table. It then determines whether the
first element of the index list is NULL (10), indicating that it should return pointers
to the index value of the first entry. The function comp_files() (11) is used again to
detect matching file names. When the matching file is found, next_file() terminates,
returning the index for the next entry (12). The value enoent, defined in errnoH, is
returned when no match is found.
7. The function named free_files(), defined in dirC (20), deallocates memory before
mgmt_poll() is called again.