SQL/MX 2.x Query Guide (G06.24+, H06.03+)
HP NonStop SQL/MX Query Guide—523728-003
2-1
2 Accessing SQL/MX Data
Access methods provide different degrees of efficiency in accessing data contained in
key-sequenced tables and indexes. Use the information in this section to understand
the various access methods used by SQL/MX:
•
Access Methods on page 2-1
•
MultiDimensional Access Method (MDAM) on page 2-12
Access Methods
This subsection describes the access methods used by the SQL compiler.
•
Storage-key access
•
Index-only access
•
Alternate index access
Each access method and its attendant cost are discussed in these subsections. An
alternative to using keyed access is a full table scan. For more information, see Full
Table Scan on page 2-5.
Storage-Key Access
The storage key refers to the physical order in which rows of the base table are stored
on disk. This key can be the primary key, clustering key, or syskey, depending on
which type of key was defined for the table.
The optimizer might choose storage-key access when:
•
The WHERE clause contains a storage-key value.
•
The estimated cost of the storage-key access is lower than the estimated cost of
an index-only or alternate index access.
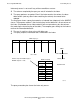
The next figure shows a query that contains a storage-key value (empnum) in the
WHERE clause. The executor goes directly to the value indicated by the information in
the WHERE clause to retrieve the row. The right portion of the figure shows the query
execution plan generated by the query.