SQL/MX 2.x Query Guide (G06.24+, H06.03+)
Accessing SQL/MX Data
HP NonStop SQL/MX Query Guide—523728-003
2-4
Alternate Index Access
Index-Only Approximate Cost
The approximate cost for index-only access is comparable to storage-key access. It
might be better because typically index tables are smaller than base tables.
Alternate Index Access
In alternate index access, a join is made between the index and the base table (an
index-base table join). Access is not made through the clustering index.
The index row is located by positioning to the requested data. When the index does not
contain all the data requested, the index is joined with the base table to provide the
requested data. When accessing the base table through an index, rows in the base
table are usually read randomly, and some blocks containing those rows might be read
more than once.
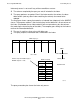
The next figure shows a query that requests all columns that satisfy the WHERE
clause. Because the index contains only a subset of the columns, a join is made
between the index and the base table to retrieve the row that satisfies the WHERE
clause. The query plan shows the nested join that joins the index (represented by the
INDEX_SCAN operator) and the base table (represented by the FILE_SCAN operator).
empnum first_name last_name deptnum jobcode salary
TABLE employee
100
Base Table
SELECT * FROM employee
WHERE deptnum = 9000;
ROOT
PARTITION_ACCESS
INDEX_SCAN
QUERY PLAN
VST023.vsd
Roger
Green 9000 100 1755000.00
337 Dinah Clark
9000 900 37000.00
deptnum empnum
9000 100
9000 900
INDEX xempdept
Index on deptnum
NESTED JOIN
PARTITION_ACCESS
FILE_SCAN