SQL/MX Programming Manual for Java
Introduction
HP NonStop SQL/MX Programming Manual for Java—523726-003
1-9
Processing an SQLJ Program
Processing an SQLJ Program
There are two methods of processing an SQLJ program:
•
Default Processing Without Module Definition Files on page 1-9
•
Processing With Module Definition Files on page 1-17
The first method is the default method of SQLJ processing in SQL/MX Release 2.x and
later product versions. The second method is the only method of SQLJ processing in
SQL/MX Release 1.8 and can be activated in SQL/MX Release 2.x by using the
-createMDF option on the command line or in a properties file. The next subsections
describe how an SQLJ program is processed according to these two methods.
Default Processing Without Module Definition Files
This method, which is the default method in SQL/MX Release 2.x and later product
versions, does not use module definition files (.m files) for SQL/MX-specific information
to be SQL compiled. Not having module definition files enables you to create and
maintain one self-contained JAR file for the entire SQLJ application. For details, see
Packaging the Program in a JAR File on page 6-5.
By default, the SQLJ translator program, sqlj.tools.Sqlj, does not generate a
module definition file during customization. Instead, the SQLJ translator program
inserts an embedded module definition in the extended profile. To produce the module,
you must use the mxCompileUserModule utility to SQL compile the embedded
module definition within the extended profile.
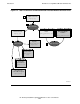
Processing an SQLJ program without module definition files involves these steps:
1. Creation of the SQLJ Source File on page 1-11
2. Translation on page 1-11
3. Compilation by the Java Compiler on page 1-12
4. Customization Without Module Definition Files on page 1-13
5. Compilation by mxCompileUserModule
on page 1-14
For the entire process, see Figure 1-1
on page 1-10 and Figure 1-2 on page 1-15.