SQL/MX Programming Manual for Java
Introduction
HP NonStop SQL/MX Programming Manual for Java—523726-003
1-11
Default Processing Without Module Definition Files
Creation of the SQLJ Source File
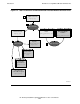
Write the source code of an SQLJ program in an SQLJ source file, which must have
the .sqlj extension. See Section 3, SQLJ Programming and Section 4, SQL/MX
Programming Considerations.
Translation
The processing of an SQLJ source file starts when you invoke the SQLJ translator
program from the command line. The SQLJ translator program, sqlj.tools.Sqlj, is
a Java program that automatically invokes translation, Java compilation, and
customization of an SQLJ program, depending on the options that you pass to it. For
more information, see SQLJ Translator Command Line on page 5-10.
The first step in processing an SQLJ program is translation, or precompilation, of the
SQLJ source file. The SQLJ translator uses the SQLJ source file (.sqlj file) to
generate these files:
•
Java Source File on page 1-11 (the .java file)
•
Profile on page 1-12 (the .ser file)
During translation, the translator parses the SQLJ source code and checks the SQLJ
syntax and the syntax and semantics of the embedded SQL statements. The translator
performs online checking of the SQL statements by using an actual NonStop SQL
database. During online checking, the translator verifies the names, scope, and data
types of the host variables in each SQL statement. The translator also checks the
syntax and semantics of each SQL statement and verifies that the referenced
database objects exist.
Because the process of translation operates according to the SQLJ standard, you can
translate an SQLJ source file by using another vendor’s SQLJ translator (as long as
you do not use vendor-specific extensions or a customizer) and port the generated files
to an HP NonStop server.
Java Source File
The Java source file (.java) contains pure Java source code. The SQLJ translator
replaces the SQLJ clauses, which contain the embedded SQL/MX statements, with
Java calls to the SQLJ run-time methods. The SQLJ run-time methods and classes
compose a standard-defined SQLJ application programming interface (API) called the
SQLJ run-time library. Calls to the SQLJ run-time library refer to entries in the profile,
which execute the associated SQL/MX statements. See Profile on page 1-12.
The Java source file also contains a class definition of the keys class, which the SQLJ
translator automatically generates, and class definitions of any SQLJ iterator and
connection context declarations that you specify in the SQLJ source file.
1
2