SQL/MX Programming Manual for Java
Introduction
HP NonStop SQL/MX Programming Manual for Java—523726-003
1-13
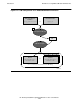
Default Processing Without Module Definition Files
Customization Without Module Definition Files
After successful translation and Java compilation, the SQLJ translator program
automatically invokes customization of the profiles (.ser) for SQL/MX. The process of
customization adds vendor-specific optimizations to each profile. For an SQL/MX-
specific implementation, the customizer:
•
Verifies the syntactic and semantic correctness of the SQL statements
•
Computes type conversion between the host variables and the referenced SQL
columns and saves this information in the extended profile
•
Produces a form of each SQL statement that is ready to be compiled by the
SQL/MX compiler
•
Expands database object names by using current settings
Customization requires access by the customizer to the metadata of the referenced
database through a JDBC connection. The customizer performs online checking of the
SQL statements by using JDBC/MX to prepare each statement and by using an actual
SQL/MX database. During online checking, the customizer checks the syntax and
semantics of each entire SQL statement and verifies that the referenced database
objects exist.
If you choose not to customize a profile, or if the customizer fails to customize a profile,
the default run time consists of dynamic JDBC calls to the database. For more
information about the default run time and dynamic SQL, see Static and Dynamic SQL
on page 4-1.
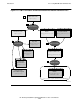
Extended Profile
The customizer extends each profile (.ser file) with SQL/MX-customized run-time
information, producing an extended profile.
The customizer instantiates the original classes of the profile and extends them with
classes that contain the SQL/MX-customized run-time information. The SQL/MX-
customized run-time information includes type conversions between the host variables
and the referenced SQL columns. The customizer stores both the original classes and
the SQL/MX customizations in the extended profile.
You can view the contents of the extended profile by using the ProfilePrinter tool.
For more information, see ProfilePrinter Tool on page 5-42.
Embedded Module Definition
The customizer uses each profile and the metadata information of each embedded
SQL statement in the profile to generate an embedded module definition. The
embedded module definition contains a form of each SQL statement that is ready to be
compiled by the SQL/MX compiler and SQL/MX-specific information related to each
SQL statement, such as the procedure header and the input and output descriptor
declarations. The embedded module definition is stored within the extended profile
4