SQL/MX Programming Manual for Java
Introduction
HP NonStop SQL/MX Programming Manual for Java—523726-003
1-14
Default Processing Without Module Definition Files
(.ser file) in an SQL/MX-specific section, keeping the original, default customization
separate as required by the SQLJ standard.
Compilation by mxCompileUserModule
After translating, customizing, and optionally packaging an SQLJ program, use the
mxCompileUserModule utility to produce the compiled SQL/MX module or modules
for the application. (To package an SQLJ program in a JAR file, see Packaging the
Program in a JAR File on page 6-5.)
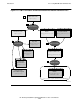
When invoked, the mxCompileUserModule utility reads the extended profile or
opens the JAR file of a packaged SQLJ application and starts reading the extended
profiles (.ser files) within it, one at a time. The mxCompileUserModule utility
instantiates the serialized Java object of each extended profile and writes the SQL
statements within the instantiated profile to a temporary file. During this process, the
mxCompileUserModule utility does not change the contents of the JAR file or the
profile.
The SQL/MX compiler (MXCMP) compiles the temporary file into a module. See SQL
Compilation on page 1-16 and Module on page 1-16. A separate MXCMP process
occurs for each profile within the JAR file, producing a set of modules for the SQLJ
application. See Figure 1-2 on page 1-15.
Note. Currently, SQL/MX does not support locally placed modules for SQLJ applications. The
modules of an SQLJ application must be stored in the /usr/tandem/sqlmx/USERMODULES
directory. Otherwise, the program will either run dynamically or return an SQL exception
indicating that the module is missing or corrupted. For more information, see SQL/MX
Compiler Errors on page 4-5.
5